All you need to know about Nuetering/ spaying of pets

puppies bonding with a vet
The surgical procedure commonly known as spaying or neutering removes the ovaries and uterus from female dogs (bitches)/cats (queens).Veterinarians widely practice and highly recommend this procedure due to its numerous health benefits and population control advantages.Veterinarians routinely perform this procedure at varying ages. At vetlit veterinary services , we advocate performing this procedure just before the first heat cycle (between 5 months to a year, depending on the breed) and beyond. This article aims to provide a comprehensive review of ovariohysterectomy.
Indication for spaying.
Various reasons indicate the need for ovariohysterectomy, including population control, prevention of unwanted pregnancies, and management of certain medical conditions.
One of the primary reasons for performing this procedure is to prevent the overpopulation of dogs/cats which can lead to strays and overcrowded animal shelters. This problem currently affects our cities (Kampala, Mbale, Wakiso, jinja, etc.) and urban centres. By spaying bitches, the risk of accidental pregnancies and contributing to this issue can be significantly reduced. Additionally, ovariohysterectomy is recommended to prevent reproductive system diseases such as pyometra a potentially life-threatening infection of the uterus. The procedure also eliminates the risk of uterine prolapse, and mammalian, ovarian and uterine tumours which can be common in older unspayed bitches. Additionally spaying eliminates the occurrence of estrus-related behavioural problems such as excessive vocalization and attraction of male dogs which can be distressing for both the bitch and her owner.
Surgical Procedure:
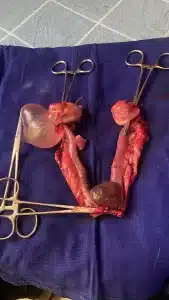
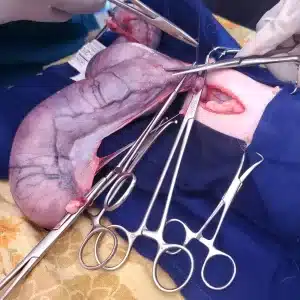
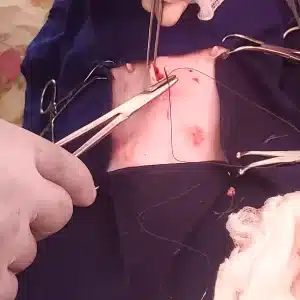
Ovariohysterectomy is typically performed under general anaesthesia. The procedure involves making a midline incision in the abdominal wall followed by careful dissection of the tissues to expose the ovaries and uterus. The blood vessels supplying these organs are ligated and the structures are then removed. Finally, the abdominal wall is sutured close.
As with any surgical procedure ovariohysterectomy in a bitch carries certain anaesthetic risks. Anaesthesia-related complications can occur including adverse reactions to anaesthetic drugs respiratory depression and cardiovascular instability. Careful pre-anaesthetic evaluation including a thorough physical examination and bloodwork is crucial in identifying any underlying health conditions that may increase the anaesthetic risk.
It is important to note that the benefits of ovariohysterectomy significantly outweigh the potential anaesthetic risks. The procedure is considered routine and has been performed on millions of bitches worldwide with excellent safety records. Veterinary professionals are well-trained in managing anaesthesia and follow strict protocols to ensure the best possible outcomes for their patients.
Postoperative Care
Proper postoperative care is essential to ensure a smooth recovery for the bitch
. Pain management is crucial as surgical pain can be significant. Painkillers are commonly used to control postoperative pain. However, it is important to note that certain breeds may be more sensitive to certain painkillers. Adequate pain control should be tailored to the individual patient and closely monitored.Activity restriction is also important during the recovery period to prevent complications such as dehiscence or incisional hernias. Bitches should be kept on leash walks and prevented from jumping or engaging in strenuous activity. Additionally, Elizabethan collars may be necessary to prevent licking or biting at the incision site.
Potential Complications
Although ovariohysterectomy is generally considered a routine procedure complications can occur. One potential complication is incisional dehiscence which is the separation of the surgical incision. This can be caused by excessive tension on the suture line or poor healing. In some cases, dehiscence may require surgical intervention to repair the incision and prevent further complications. Another potential complication is the development of urinary incontinence which may occur due to the removal of the ovaries. The ovaries produce hormones that help maintain the tone of the urethral sphincter. In the absence of these hormones, some bitches may develop urinary incontinence. However, this complication can often be managed with medication.
In conclusion, ovariohysterectomy in a bitch is a commonly performed surgical procedure that offers numerous advantages. It eliminates the risk of unwanted pregnancies prevents life-threatening uterine infections reduces the incidence of mammary tumors and addresses problematic estrus-related behaviors. Although there are inherent anesthetic risks associated with any surgical procedure proper pre-anesthetic evaluation and modern anesthetic protocols help minimize these risks. Veterinary professionals play a vital role in ensuring the safe and successful execution of ovariohysterectomy benefiting the overall health and well-being of your canine friend..